VNet is an Azure Resource that represents a virtual network in Azure. It is a logical isolation of the Azure cloud dedicated to your subscription. You can deploy and manage virtual machines (VMs), and read more about Virtual Machines in Azure, and other resources in a VNet.
What is Default VNet?
The Default VNet is the pre-created and default virtual network in each Azure subscription. All newly deployed resources are automatically connected to the Default VNet unless you specifically create and connect them to a different one. The address space for the Default VNet is always 10.0.0.0/16, and it cannot be changed without deleting the VNet and then recreating it.
Features of VNet Traffic Monitoring
Flow Logs: Capture information about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in a VNet.
NSG Flow Logs: View logs for denied traffic by using Network Watcher’s NSG flow logs capability.
Azure Monitor for VMs: Collect VM performance and activity data at scale to monitor the health and availability of your VMs.
Azure Monitor Logs: Collect and analyze activity and diagnostic logs from Azure resources to help you understand how they’re being used.
There are two types of traffic that can flow in and out of a VNet:
East-west traffic: This refers to the communication between VMs within the same VNet, regardless of whether they’re in the same region or different regions.
North-south traffic: This refers to the communication between a VM in a VNet and resources outside the VNet, such as internet resources, on-premises locations, or other Azure VNets.
How does the Creating VNet in Azure?
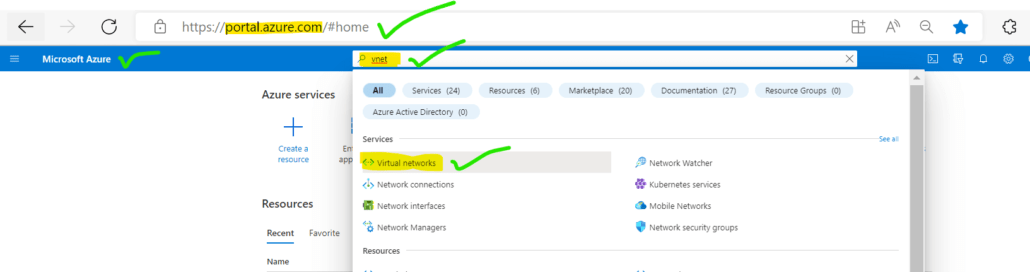
Step 1: 1 Go to the Azure portal and search for Vnet and open the virtual network.
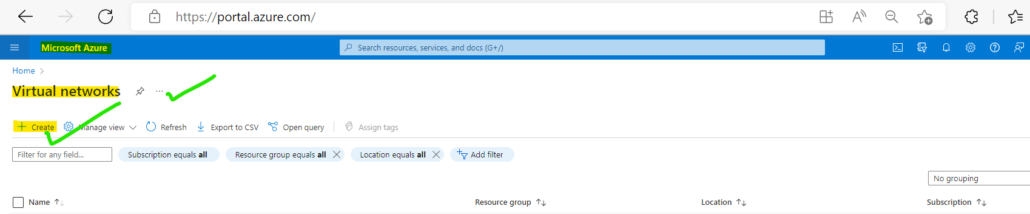
Step 2: Now click on create new virtual network but before this, you should have a plan of your network requirement and what CIDR range you want to use.
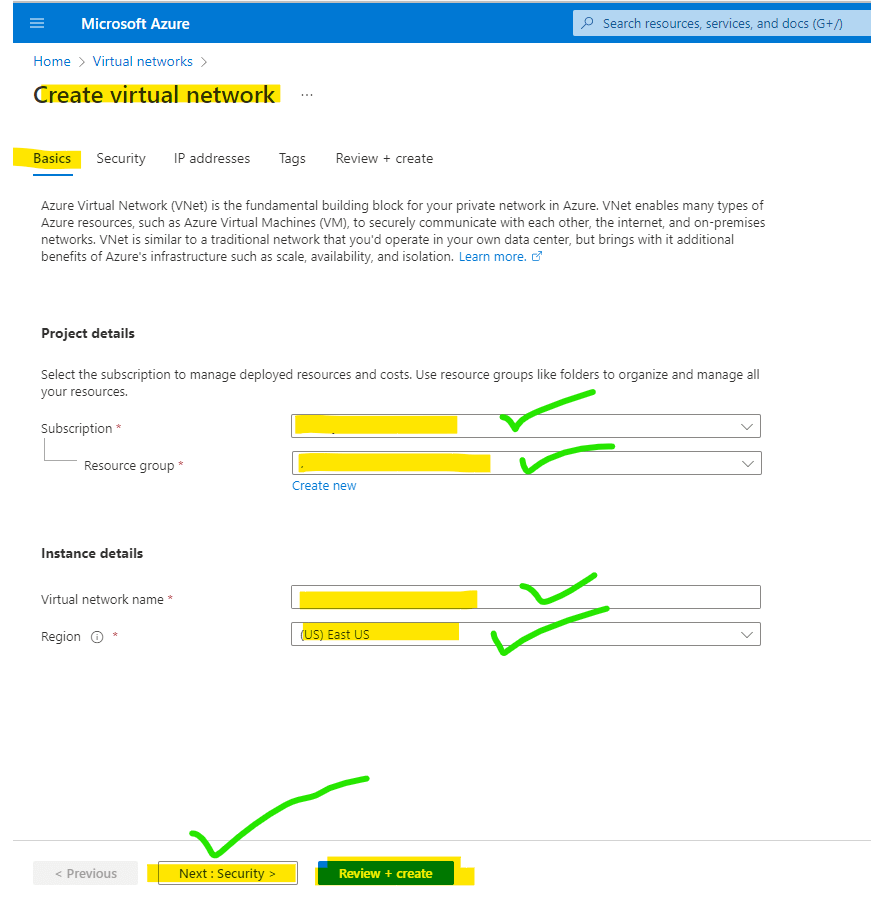
Step 3: Select subscription and resource group and add the name. Go next to security.
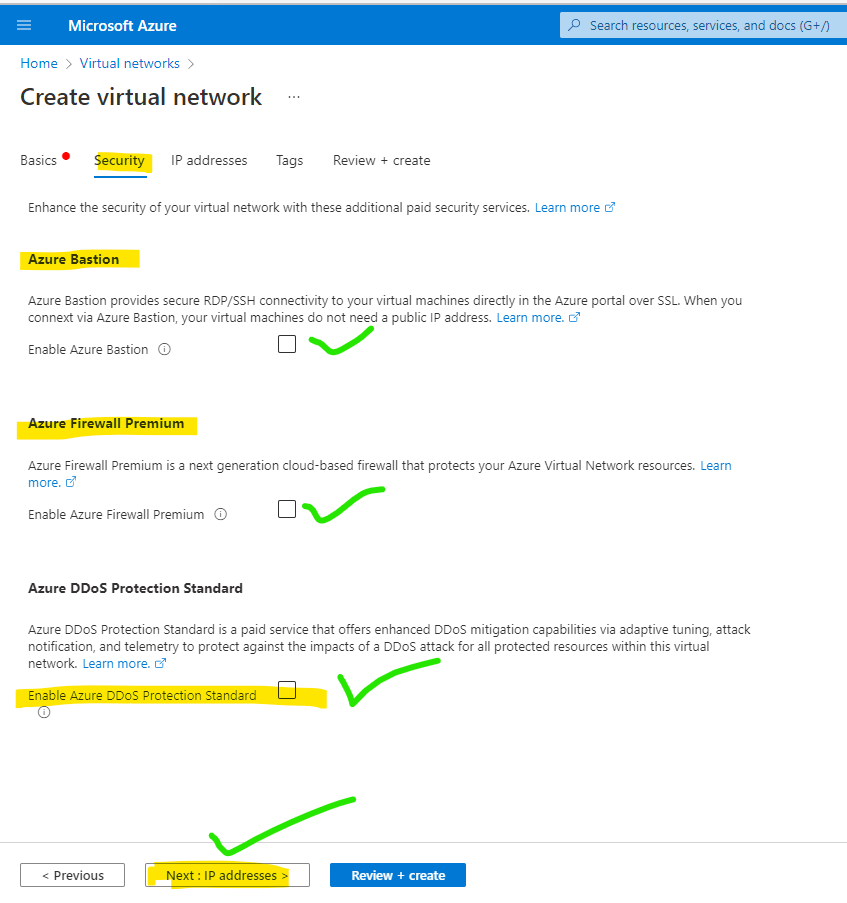
Step 4: Add security parameters according to your network’s need for DDOS. Click on next.
Step 5: Add CIDR range according to your need and remove or delete the default one then click on review and create. If you need a tag then add it to validate passed and VNET will be created.

Step 6: Now that VNET is created open it and check.
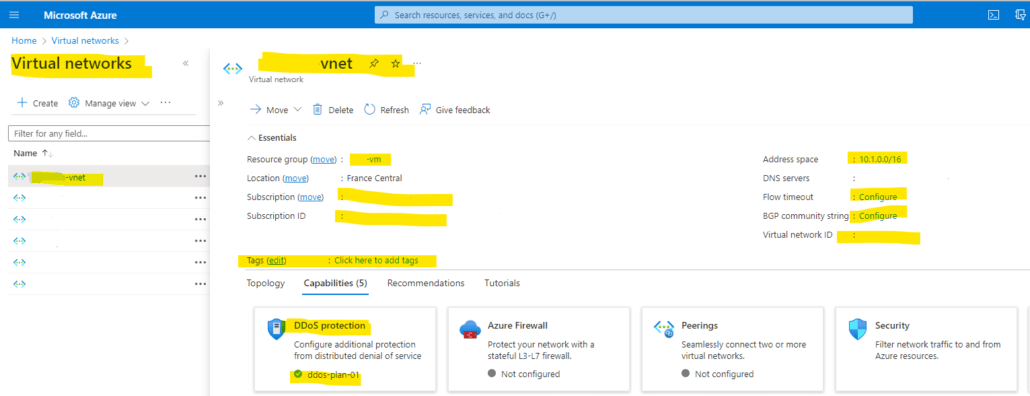
It takes a few minutes to create the VNet. You see it in the list of resources on the left side of the portal. Select the resource to open its overview page.
How does VNet work in different Resource groups and Zones?
You can create a VNet in any resource group within your Azure subscription. After you create it, you can move resources into or out of the VNet without affecting other resources in the resource group.
When you deploy a VM or other workloads into a VNet, you can optionally place them in an availability zone for added resiliency.
Limitations of VNet
- The maximum number of VMs per VNet is 100.
- The maximum number of address spaces that can be assigned to a VNet is 200.
- The maximum number of route tables per VNet is 100.
- The maximum number of network security groups per VNet is 100.
- The maximum number of security rules per network security group is 200.
- The maximum number of virtual networks that can be peered at with a given VNet is 100.
- The maximum number of inbound and outbound rules per load balancer is 650.
- The maximum number of public IP addresses per load balancer is 150.
- The maximum number of load balancers per VNet is 10.
- The maximum number of application gateways per VNet is 5.
- The maximum number of VPN gateways per VNet is 2.
- The maximum number of Azure Firewalls per VNet is 4.

