The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the interconnectedness of physical objects and devices that are equipped with sensors and other technology that allows them to collect and exchange data. IoT protocols are the rules and standards that govern how these devices communicate with each other.
What are the Different Types of IoT Protocols?
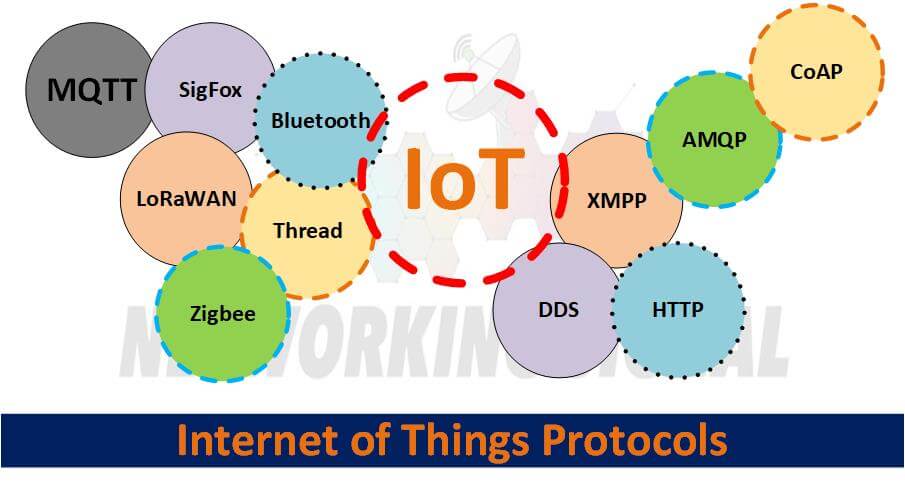
There are a number of different types of IoT protocols, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most popular protocols include:
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): BLE is a wireless communication standard that is designed for low power consumption. It is often used in devices such as fitness trackers and heart rate monitors.
Zigbee: Zigbee is another low-power wireless communication standard that is popular in IoT devices. It has a longer range than BLE and can be used for applications such as home automation.
Thread: Thread is a mesh networking protocol that was developed by Google and Nest. It is designed for low power consumption and is often used in devices such as thermostats and security cameras.
LoRaWAN: LoRaWAN is a long-range wireless communication standard that is popular in IoT applications such as smart city infrastructure and agricultural monitoring.
Sigfox: Sigfox is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) protocol that is designed for IoT applications. It has a very long range and can be used for devices such as water meters and electricity meters.
MQTT: MQTT is a lightweight publish/subscribe messaging protocol that is often used in IoT applications. It is designed for low bandwidth and can be used in devices such as weather stations.
HTTP: HTTP is the standard protocol for communication on the World Wide Web. It can be used for IoT applications but is not as efficient as some of the other protocols.
DDS: The Data Distribution Service (DDS) is a real-time publish/subscribe messaging protocol that is often used in industrial and military applications.
AMQP: The Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) is an open standard for message queuing that is often used in financial applications.
XMPP: Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) is an open standard for instant messaging that can be used for IoT applications.
CoAP: The Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) is a web transfer protocol that is designed for use in constrained devices such as sensors.
What are the Uses of Internet of Things Protocols?
IoT protocols are used in a variety of applications, including:
Smart homes: Smart home devices such as thermostats, security cameras, and door locks often use IoT protocols to communicate with each other.
Connected cars: Many modern cars are equipped with sensors and other technology that allows them to connect to the internet. These connected cars often use IoT protocols to exchange data with other devices.
Industrial applications: Manufacturing plants and other industrial facilities often use IoT protocols to monitor equipment and track inventory.
What are the Benefits of Internet of Things Protocols?
IoT protocols offer a number of benefits, including:
Increased efficiency: IoT protocols can help to increase the efficiency of processes by automating tasks and providing real-time data.
Improved safety: IoT protocols can help to improve safety by providing data that can be used to identify potential hazards.
Reduced costs: IoT protocols can help to reduce costs by eliminating the need for manual tasks and improving asset management.
What are the Challenges of Internet of Things Protocols?
IoT protocols can present a number of challenges, including:
Interoperability: One of the biggest challenges with IoT protocols is interoperability, or the ability of devices from different manufacturers to work together. This can be a challenge because each manufacturer may use a different protocol.
Security: Another challenge with IoT protocols is security. Because IoT devices are often connected to the internet, they can be susceptible to hacking and other security threats.
Lack of standards: There is currently no single standard for IoT protocols. This can make it difficult for devices from different manufacturers to work together.
What’s Next for Internet of Things Protocols?
IoT protocols are constantly evolving. The future of IoT protocols will likely include:
More standards: As the IoT market grows, there will likely be more standards developed to help improve interoperability.
Better security: As the number of IoT devices grows, so does the need for better security. Manufacturers will likely continue to develop new ways to protect IoT devices from hacking and other security threats.
Increased adoption: IoT protocols are expected to see increased adoption in a variety of industries, including smart homes, connected cars, and industrial applications.