What Standard TCP Port Does the BGP Service Operate On?
The Standard TCP port used for the BGP service is 179. BGP is a path vector protocol that enables two or more autonomous systems to communicate and exchange routing information. It is an external gateway protocol (EGP) used to exchange routing and reachability information between different networks.
What is BGP Service 179?
BGP Service 179 ( also known as TCP port 179 ) is the standard Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port number that is assigned to the border gateway protocol (BGP). BGP allows two or more autonomous systems (ASs) such as ISPs and corporations to exchange routing information. It uses TCP for the reliable transport of messages between peers in the same AS or between different ASs.
What Are the Benefits of Using BGP Service 179?
Here are some of the key benefits of using BGP Service 179:
- Reduced latency as it is faster and more reliable than other routing protocols.
- Highly secure communication between autonomous systems reduces the chances of unauthorized access.
- Easily accessible information on peers, allowing for quick route changes or modifications when needed.
- High scalability, allowing for the efficient exchange of routing information over large networks.
- More flexible route selection process based on criteria such as AS path length, origin, or cost.
- Ability to support multiple network layer protocols and address families.
How Does TCP Port Operate in BGP?
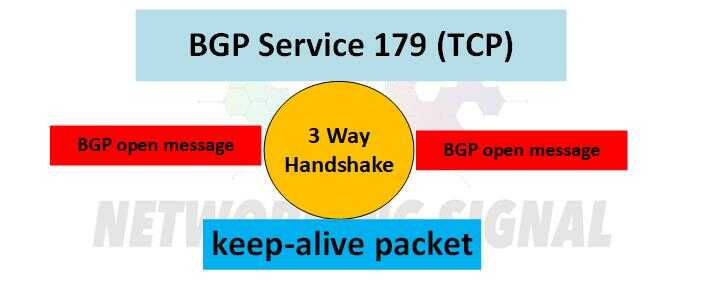
The TCP port 179 is responsible for the reliable exchange of BGP messages between routers. It uses the TCP three-way handshake process to initiate a connection and then sends keepalive packets to ensure that the connection is maintained. The BGP session can be terminated by either side using a notification message. BGP messages are sent in multiples of 4 bytes and are compressed before transmission.
Example:
- Router A sends a BGP open message to Router B via TCP Port 179.
- Router B responds with an acknowledgment and sends a keep-alive packet to ensure the connection is maintained.
- If the keep-alive packet is not received, then Router A will resend its open message.
- Once the session is established, router A sends the route update messages and other BGP messages over TCP Port 179.
- Router B will process these messages and respond accordingly.
- The session can be terminated by either side using a notification message.

